Organization levels of matter
Explore the hierarchy of matter and life, from the tiniest atoms and cells to complex tissues, organs, and complete living organisms.
1 The Building Blocks: Atoms and Molecules
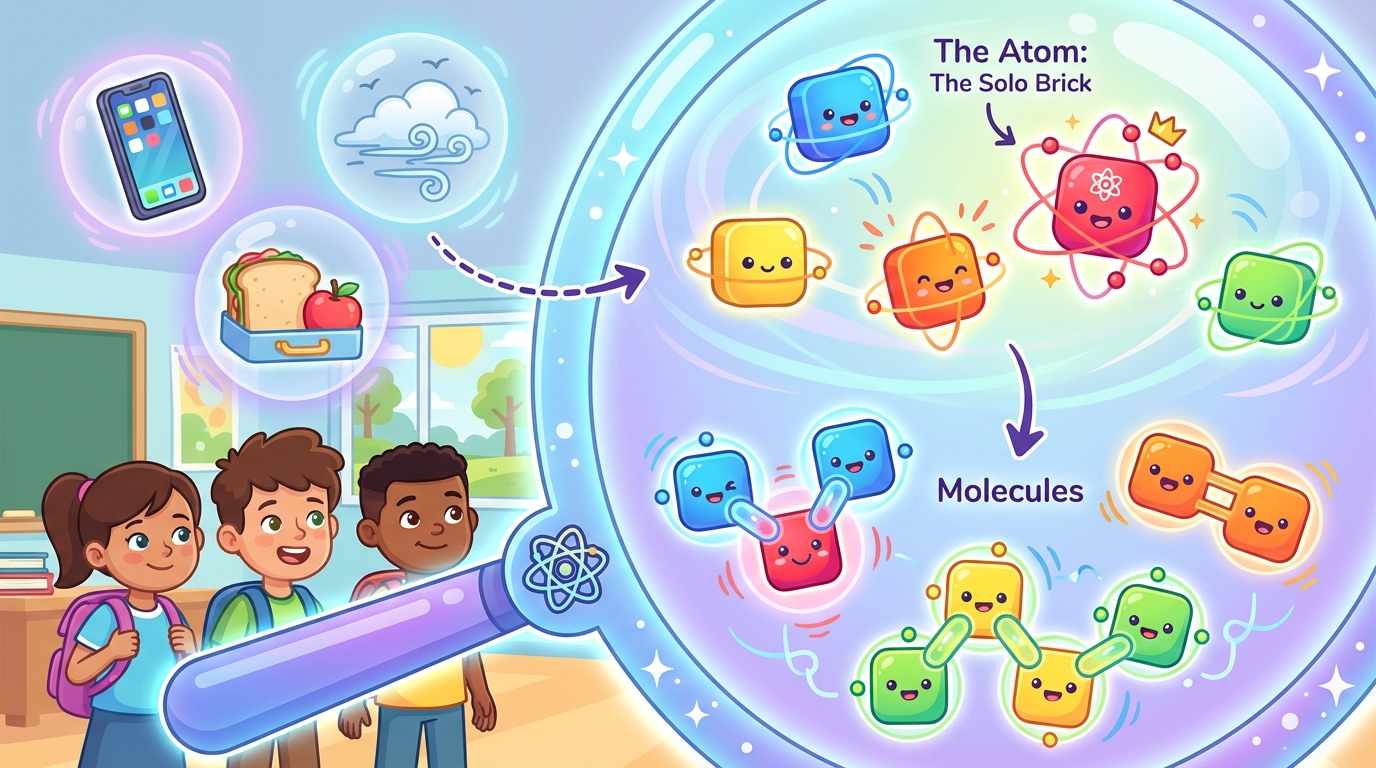
Everything around you—your phone, your lunch, and even the air you breathe—is made of matter. But if we used a super-powerful microscope to zoom in, what would we see?
Think of an atom like a single LEGO® brick. It is the smallest unit of an element. If you cut a piece of pure gold into smaller and smaller pieces, the smallest piece you can have that is still gold is one atom.
- Size: Super tiny! Millions fit on a pinhead.
- Examples: Oxygen (O), Carbon (C), Iron (Fe).
When two or more atoms join together (bond), they form a molecule. It's like snapping different LEGO® bricks together to build a specific shape.
- Structure: Can be atoms of the same type or different types.
- Examples: Water (H₂O), Carbon Dioxide (CO₂).
💧 Real-Life Example: Water
Water is the perfect example of teamwork! One water molecule is made of three atoms: 2 Hydrogen atoms + 1 Oxygen atom. Scientists write this as H₂O.
| Feature | Atom | Molecule |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Basic building block of matter | Group of bonded atoms |
| Visibility | Needs powerful microscopes | Also microscopic, but larger |
| Analogy | A single letter (A, B, C) | A word (CAT, DOG) |
Key Facts
2 The Basic Unit of Life: Cells
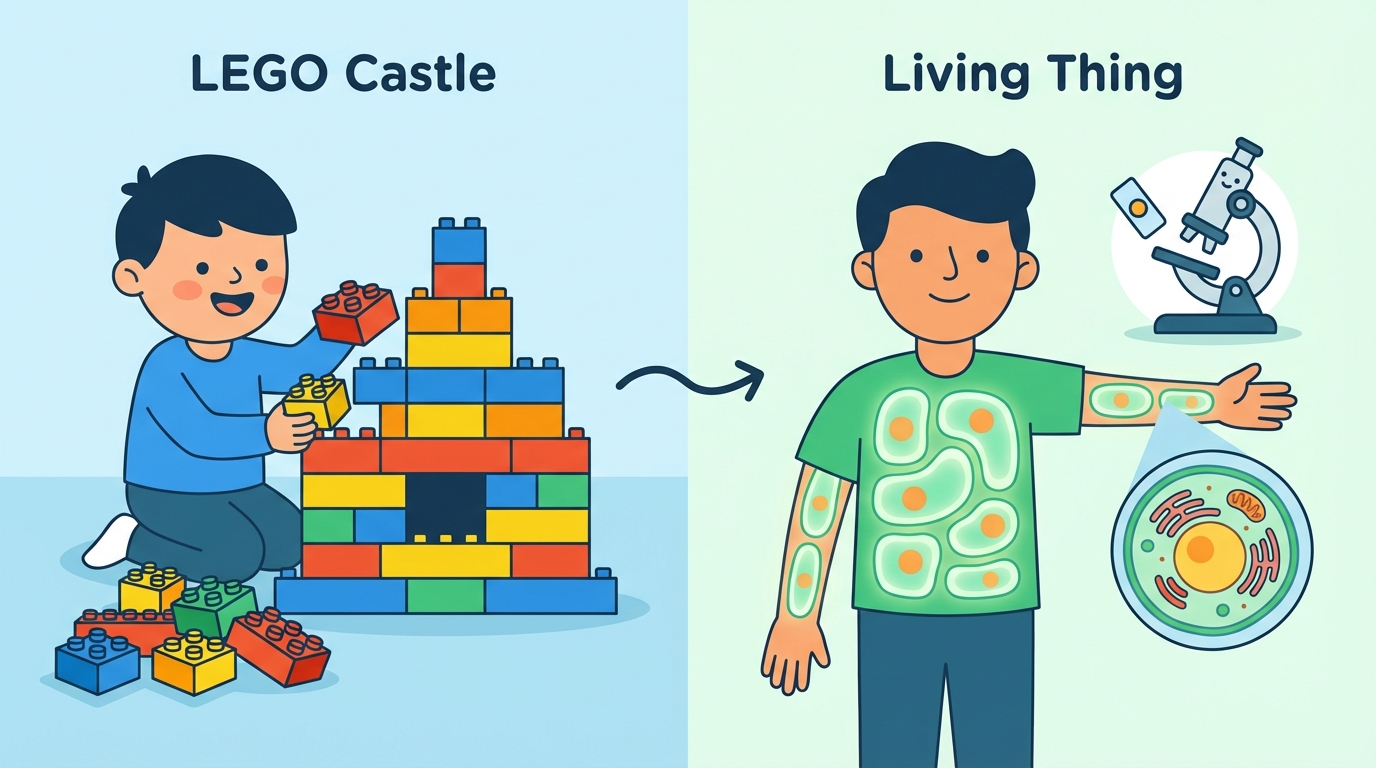
Have you ever played with LEGOs? 🧱 Just like a giant castle is built from tiny bricks, every living thing is built from tiny parts! This is called the Organization of Matter.
🔬 From Small to Big: The Ladder of Life
Nature is organized in levels. It starts with non-living things and moves up to living creatures.
- Atoms: The tiniest building blocks of everything (like Oxygen). ⚛️
- Molecules: Atoms joined together (like Water or DNA). 💧
- Cells: The first level where life begins! A cell is the basic unit of structure and function. 🦠
- Tissues, Organs, & Systems: Groups of cells working together.
🏫 The School Analogy
Understanding these levels can be tricky, so let's imagine your body is like a School:
| Level of Organization | School Analogy | Real Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cell | One Student 🧑🎓 | Muscle Cell |
| Tissue | A whole Class 👨🏫 | Muscle Tissue |
| Organ | The Gym Building 🏟️ | Stomach |
| Organ System | All the buildings together 🏘️ | Digestive System |
| Organism | The Whole School District 🚌 | You! (Human) |
Key Facts
3 Teaming Up: From Cells to Tissues
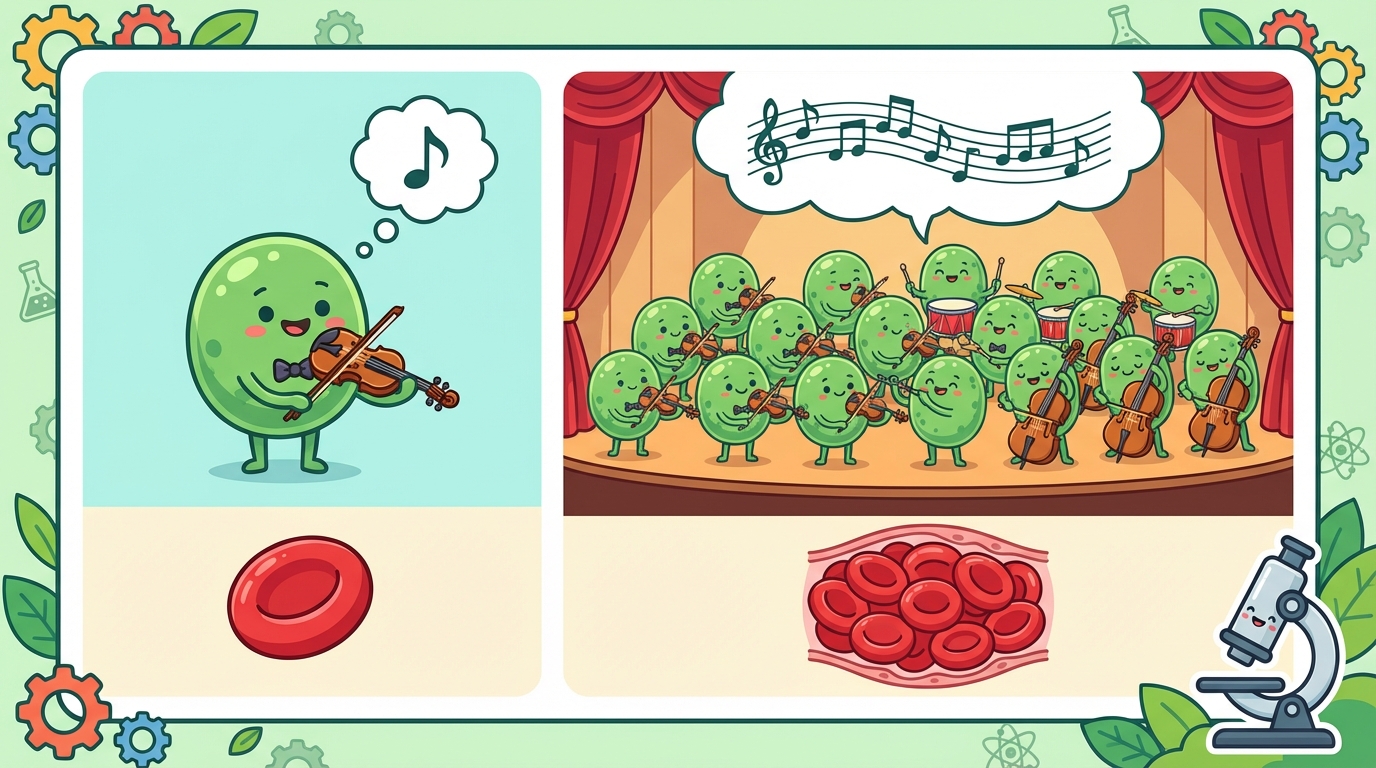
Imagine a single musician playing a violin. Beautiful, right? 🎻 Now, imagine 50 musicians playing together. That's an orchestra! 🎼 Cells are just like those musicians. They can do simple things alone, but when they team up, they can build amazing things.
The 4 Main Types of Animal Tissues
Just like a sports team has players with different positions (goalie, striker, defender), your body has different tissues for different jobs:
Job: Movement.
These cells can contract (shorten) and relax. They help you run, jump, and even help your heart beat!
Job: Messaging.
Found in your brain and nerves. These cells send electrical signals like text messages throughout your body.
Job: Protection.
These cells pack tightly together like a shield. Your skin is the best example!
Job: Support.
It holds body parts together. Examples include bone, fat, and even blood!
🤔 Think About It: The Brick Wall
If a Cell is a single brick 🧱... then a Tissue is the whole wall! 🏠
Key Facts
4 Complex Structures: Organs and Systems
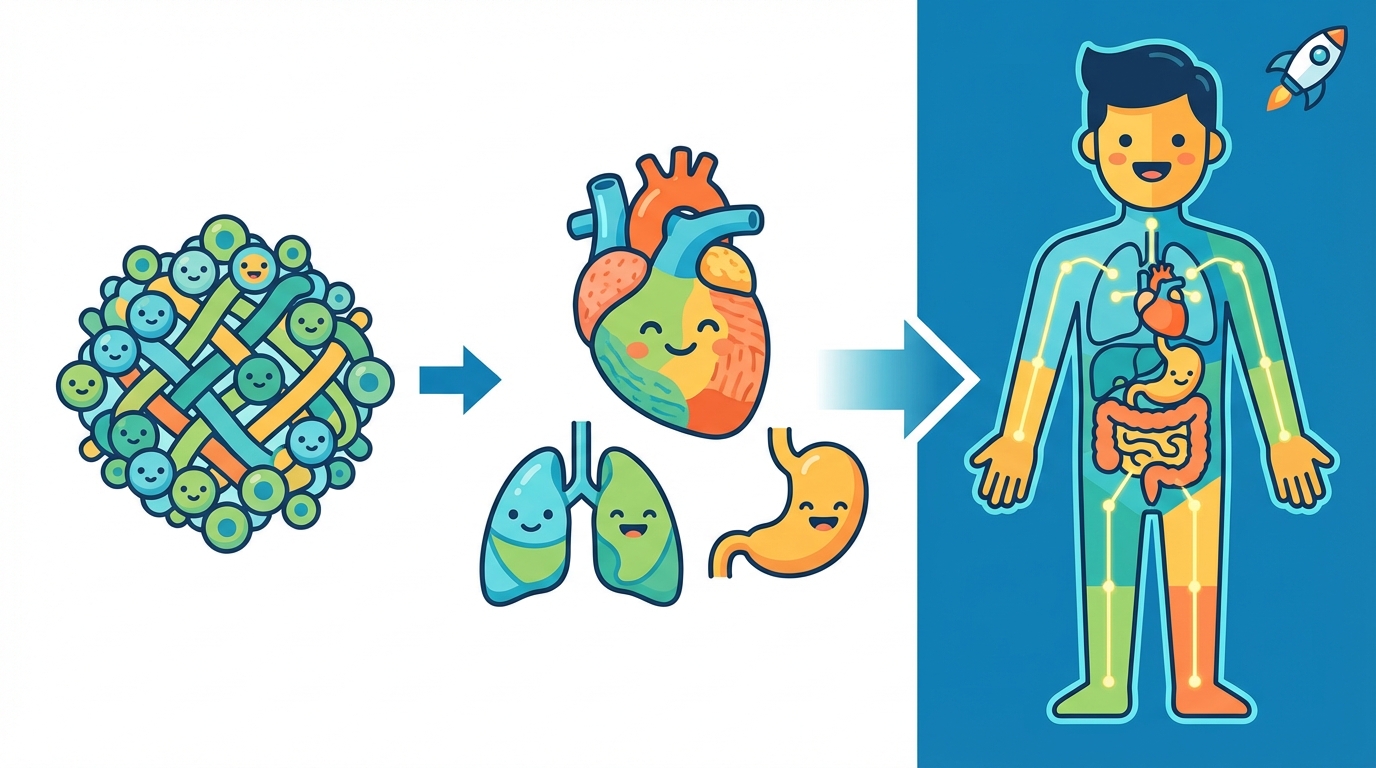
🚀 Level Up!
We already know that cells group together to form tissues. But what happens next? It's time to build bigger things! Tissues combine to create organs, and organs team up to build systems.
Imagine you are building a LEGO castle. If a tissue is a wall made of bricks, an organ is the whole tower! An organ is a structure made of two or more different types of tissues working together to do a specific job.
Example: The Heart
The heart isn't just muscle. It contains:
- 💪 Muscle tissue to pump blood.
- 🔗 Connective tissue to hold it together.
- ⚡ Nervous tissue to control the beat.
A system (or organ system) is like a sports team. A single player (organ) is great, but they need teammates to win the game. A system is a group of organs that work together to perform major body functions.
Example: The Digestive System
It takes a whole team to turn a pizza into energy:
- 👄 Mouth & Esophagus
- 🥣 Stomach
- ➰ Intestines
🔍 Quick Comparison: Organ vs. System
| Level | Made of... | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Organ | Different Tissues | 🫁 Lungs, Brain, Leaf (plants) |
| System | Different Organs | 🌬️ Respiratory, 🧠 Nervous, 🌱 Root System |
Key Facts
5 The Big Picture: The Organism

We have reached the top of the ladder! 🏆 An organism is a complete living thing capable of surviving on its own.
Think of an organism as a finished LEGO® castle. You started with individual bricks (cells), built walls (tissues), created towers (organs), and connected them with bridges (systems). Now, you have the whole castle!
An organism isn't just a bag of parts. It is a coordinated team. Your heart, lungs, brain, and stomach all talk to each other to keep you alive and healthy. This balance is called homeostasis.
One Cell vs. Trillions of Cells 🦠🐘
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Unicellular | The entire organism is just one cell that does everything (eats, moves, reproduces). | Bacteria, Amoeba |
| Multicellular | The organism is made of many specialized cells working together in systems. | Humans, Sunflowers, Whales |
Key Facts
6 Key Vocabulary
Master these important terms for your exam:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Atom
Átomo |
The smallest unit of matter that makes up everything around us.
La unidad más pequeña de materia que compone todo lo que nos rodea. |
|
Molecule
Molécula |
A group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
Un grupo de dos o más átomos unidos por enlaces químicos. |
|
Cell
Célula |
The basic unit of structure and function in all living things.
La unidad básica de estructura y función en todos los seres vivos. |
|
Tissue
Tejido |
A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function.
Un grupo de células similares que trabajan juntas para realizar una función específica. |
|
Organ
Órgano |
A structure made up of different types of tissues working together.
Una estructura formada por diferentes tipos de tejidos que trabajan juntos. |
|
Organ System
Sistema de órganos |
A group of organs that work together to perform a major body function.
Un grupo de órganos que trabajan juntos para realizar una función corporal importante. |
|
Organism
Organismo |
A complete living thing that can carry out all basic life processes.
Un ser vivo completo que puede llevar a cabo todos los procesos vitales básicos. |
|
Unicellular
Unicelular |
An organism made of only one single cell.
Un organismo formado por una sola célula. |
|
Multicellular
Multicelular |
An organism made of many cells.
Un organismo formado por muchas células. |
|
Structure
Estructura |
The way parts are arranged or put together to form a whole.
La forma en que las partes están organizadas o unidas para formar un todo. |
|
Function
Función |
The specific job or activity that a part of an organism does.
El trabajo o actividad específica que realiza una parte de un organismo. |
|
Hierarchy
Jerarquía |
An organization system where things are ranked one above another.
Un sistema de organización donde las cosas se clasifican una encima de la otra. |
|
Specialization
Especialización |
When cells develop specific structures to perform specific jobs.
Cuando las células desarrollan estructuras específicas para realizar trabajos específicos. |
|
Microscopic
Microscópico |
Something so small it can only be seen with a microscope.
Algo tan pequeño que solo se puede ver con un microscopio. |
|
Complex
Complejo |
Made of many different and connected parts.
Compuesto por muchas partes diferentes y conectadas entre sí. |
Time to Practice!
There are 7 questions waiting for you. Questions are shuffled each attempt.
Take the Quiz