Properties of Matter
Explore what the universe is made of, from atoms and states of matter to density and chemical changes.
1 What is Matter?
🌍 Look around you! Your desk, your lunch, the water you drink, and even the air you breathe...
The Big Definition
Matter is anything that has mass (it weighs something) and takes up space (volume).
✅ Yes, this is Matter!
- 🍕 Pizza: It has weight and takes up space on your plate.
- 🎮 Video Game Console: It's a solid object you can hold.
- 🎈 Air inside a balloon: Even though you can't see it easily, air takes up space!
❌ No, this is NOT Matter
- 💡 Light: It is energy, not stuff.
- 🔥 Heat: You can feel it, but it doesn't have mass.
- 💭 Thoughts: They are in your brain, but they don't weigh anything!
Key Facts
2 Atoms and Molecules: The Building Blocks
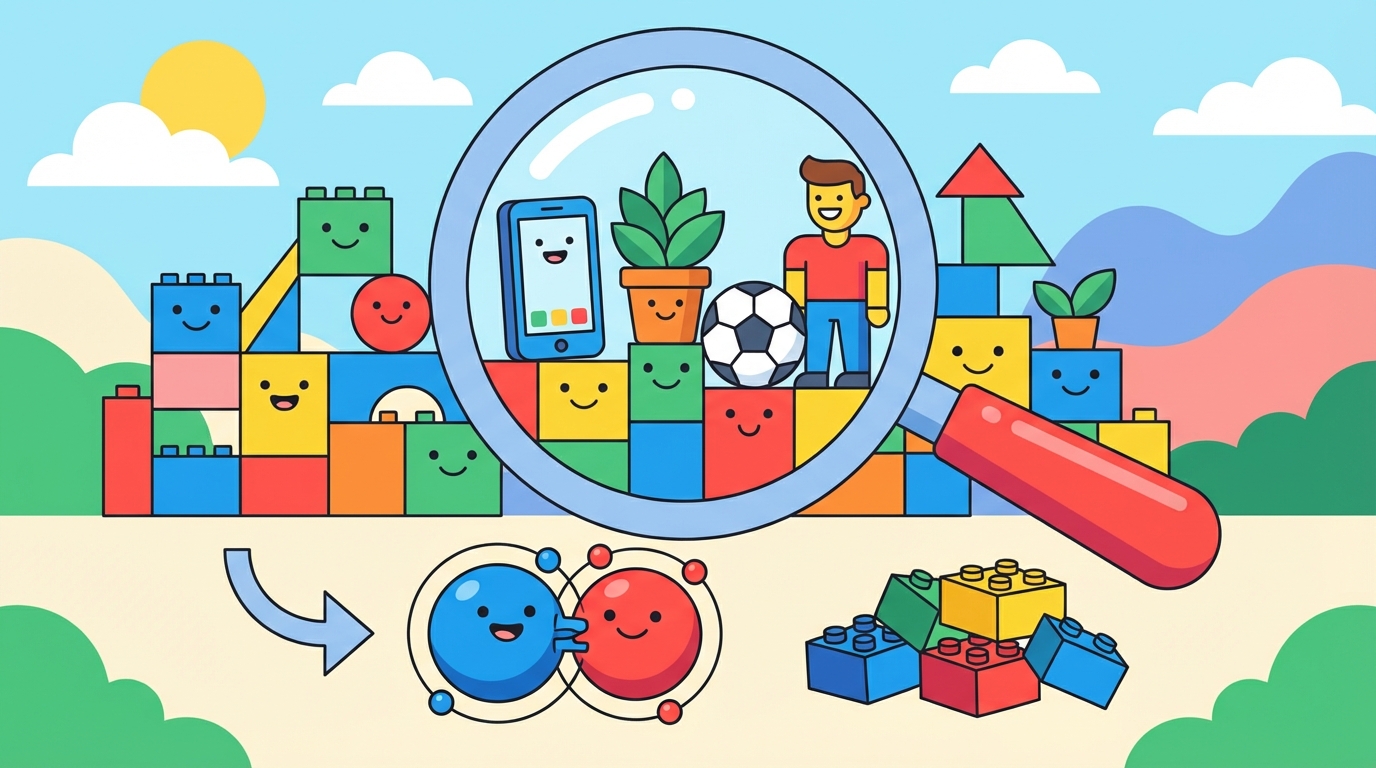

Everything around you—your phone, the air, even you—is made of matter. But if we zoomed in super close, what would we see? Let's find out! 🔬
🧱 The LEGO® Analogy
Think of the universe like a giant LEGO® castle. If you take the castle apart, you end up with individual bricks. In science:
- The Atom is the individual brick.
- A Molecule is a small structure made by snapping a few bricks together.
⚛️ What is an Atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter. It is the basic building block of everything. There are over 100 different types of atoms (elements), like Oxygen, Carbon, and Gold.
Fun Fact: A single grain of sand contains more atoms than there are grains of sand on a whole beach!
⚗️ What is a Molecule?
A molecule is made when two or more atoms join (bond) together. They act like best friends holding hands tightly.
Example: Water is a molecule called H₂O. It is made of 2 Hydrogen atoms and 1 Oxygen atom stuck together.
| Feature | Atom ⚛️ | Molecule ⚗️ |
|---|---|---|
| Size | Tiny! The smallest piece. | Bigger (made of combined atoms). |
| Visibility | Invisible to the eye. | Usually invisible, but bigger. |
| Example | Oxygen (O) | Oxygen Gas (O₂) or Water (H₂O) |
Key Facts
3 The Three Main States of Matter

Everything around you is made of matter, but matter doesn't always look the same! It usually exists in one of three forms called states: Solid, Liquid, or Gas. 🧊💧💨
🔬 The Particle Party
Think of particles (atoms and molecules) like students in a classroom. Their behavior determines the state of matter!
Particles are packed tightly together in a neat pattern. They can't move around, they just vibrate in place.
- Definite Shape ✅
- Definite Volume ✅
- Example: Ice, Rock, Wood
Particles are close together but can slide past one another. They flow to fit their container.
- No Definite Shape ❌
- Definite Volume ✅
- Example: Water, Milk, Honey
Particles are far apart and move very fast! They spread out to fill all available space.
- No Definite Shape ❌
- No Definite Volume ❌
- Example: Air, Steam, Helium
Quick Comparison Table
| Property | Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | Fixed | Takes container shape | Fills container |
| Volume | Fixed | Fixed | Changes (Expands) |
| Energy | Low 🔋 | Medium 🔋🔋 | High 🔋🔋🔋 |
Key Facts
4 Phase Changes: From Ice to Steam
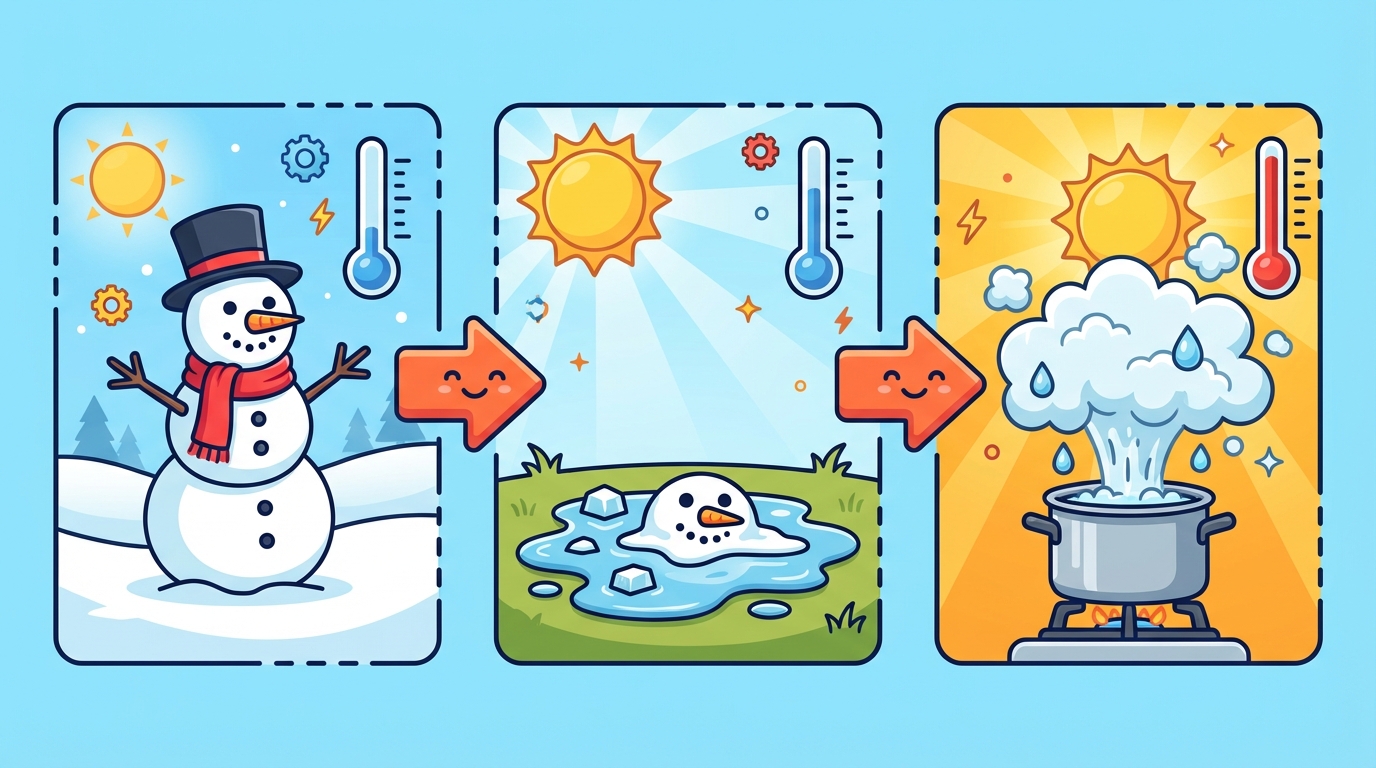
Have you ever watched a snowman disappear? ⛄ He didn't run away; he just changed his phase! Matter changes its state when we add or remove energy (heat).
Particles move faster!
- Melting: Solid ➝ Liquid.
Example: Ice cream melting on a hot day. 🍦 - Evaporation: Liquid ➝ Gas.
Example: A puddle drying up after rain. 🌦️
Particles slow down!
- Freezing: Liquid ➝ Solid.
Example: Making fruit popsicles in the freezer. 🧊 - Condensation: Gas ➝ Liquid.
Example: Fog forming on a bathroom mirror. 🚿
| Process | Start State | End State | Energy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Melting | Solid | Liquid | Added (+ Heat) |
| Freezing | Liquid | Solid | Removed (- Heat) |
| Boiling | Liquid | Gas | Added (+ Heat) |
| Condensation | Gas | Liquid | Removed (- Heat) |
Key Facts
5 Physical Properties You Can Observe
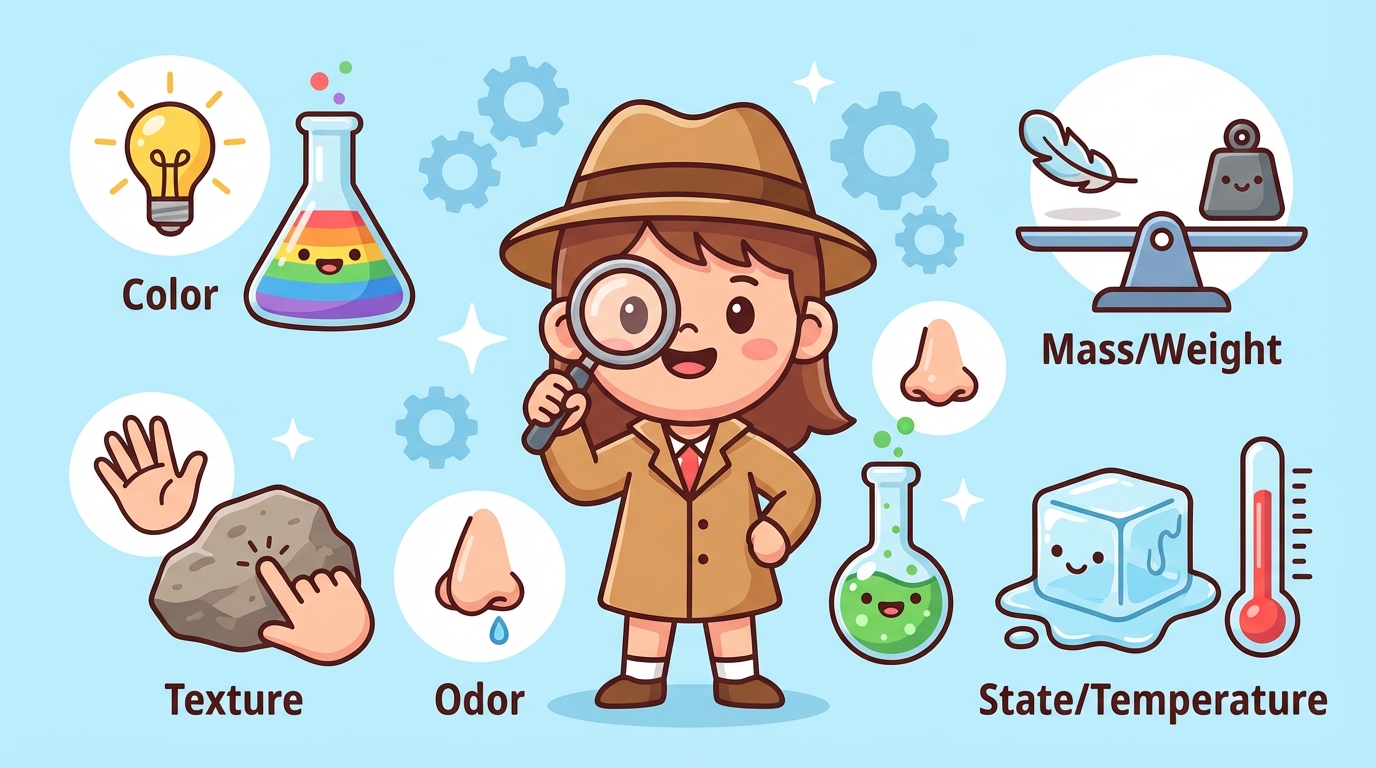
Imagine you are a Science Detective 🕵️♀️! Observable physical properties are the clues you gather using your five senses to identify matter without changing what it is.
✨ What can we observe?
We don't always need rulers or scales. Often, we just need our eyes, hands, and nose to describe what an object is like.
Color: Is the object red, blue, or colorless? This is often the first thing we notice.
Luster (Shininess): How does light hit the object?
- 🌟 Shiny (Metallic): Like a new penny or aluminum foil.
- 🌑 Dull: Like a piece of chalk or wood.
Texture: How does the surface feel?
Hardness: Is it soft like a marshmallow or hard like a rock?
👃 What about Smell?
Odor is a powerful property! Vinegar has a pungent (strong) smell, while a vanilla bean smells sweet.
⚠️ Safety Tip: Never taste chemicals in a lab to check properties!
Key Facts
6 Understanding Density
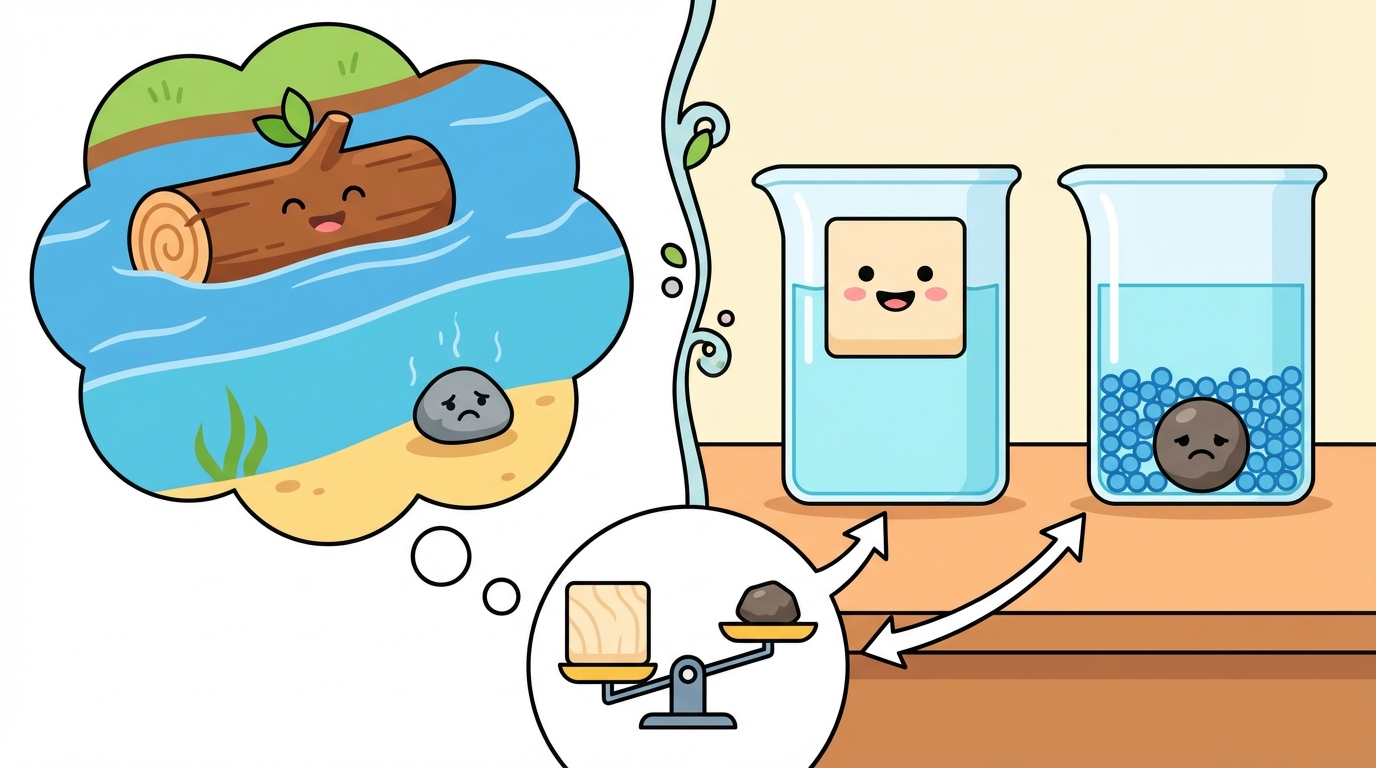
Have you ever wondered why a giant wooden log floats in a river, but a tiny pebble sinks to the bottom? 🤔 It is not just about weight; it is about Density!
📦 What is Density?
Density describes how much mass is packed into a specific volume (space). Imagine two identical suitcases:
Packed with heavy books.
High Density
Filled with fluffy pillows.
Low Density
Both take up the same space, but Suitcase A has more matter packed inside!
Density = Mass ÷ Volume
🌊 Sink or Float?
Water is our measuring stick! Water has a density of exactly 1 g/cm³.
| Object | Density | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 🍎 Apple | ~0.9 g/cm³ | Floats (Less than 1) |
| 🧱 Brick | ~1.9 g/cm³ | Sinks (More than 1) |
| 🧊 Ice Cube | ~0.92 g/cm³ | Floats (Just barely!) |
Key Facts
7 Chemical Properties and Reactivity
Think of physical properties as a person's outfit 👕 (what they look like), and chemical properties as their personality 🧠 (how they act). You can't see a chemical property just by looking at a substance; you have to see how it reacts to change!
Common Chemical Properties
This is the ability of a substance to burn. When wood burns, it turns into ash and smoke. It's no longer wood! 🪵
Have you ever seen a rusty bike? That is iron reacting with oxygen in the air. The red rust is a new substance called iron oxide.
How easily a substance reacts with others. Baking soda reacts fast with vinegar to make bubbles (gas)!
Comparison: Physical vs. Chemical
| Property Type | Question to Ask | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Can I observe it without changing what it is? | Melting ice 🧊 (It's still water!) |
| Chemical | Does it turn into something new? | Burning paper 📄 (It turns to ash!) |
🗽 Fun Fact: The Statue of Liberty is made of copper (like a penny). It turned green because of a chemical property called reactivity—the copper reacted with the air to form a green layer called patina!
Key Facts
8 Physical vs. Chemical Changes

Matter is always changing! But not all changes are the same. We classify them into two main teams: Physical and Chemical. 🧪
In a physical change, the appearance changes, but the substance stays the same. No new matter is created!
- ✂️ Tearing paper: It is still paper.
- 💧 Melting ice: It is still water (H₂O).
- 🧂 Dissolving salt: You can evaporate the water to get the salt back.
In a chemical change, a chemical reaction happens and a new substance is formed. It is usually hard to reverse.
- 🪵 Burning wood: Turns into ash and smoke.
- 🔩 Rusting iron: Metal turns into orange rust.
- 🥞 Baking pancakes: Batter turns into fluffy cake.
🕵️ How to spot a Chemical Change?
Look for these clues (evidence) that a reaction is happening:
| Feature | Physical Change | Chemical Change |
|---|---|---|
| Identity | Stays the same | Changes (New substance) |
| Reversibility | Often reversible | Usually irreversible |
| Example | Slicing bread 🍞 | Toasting bread 🥪 |
Key Facts
9 The Law of Conservation of Mass
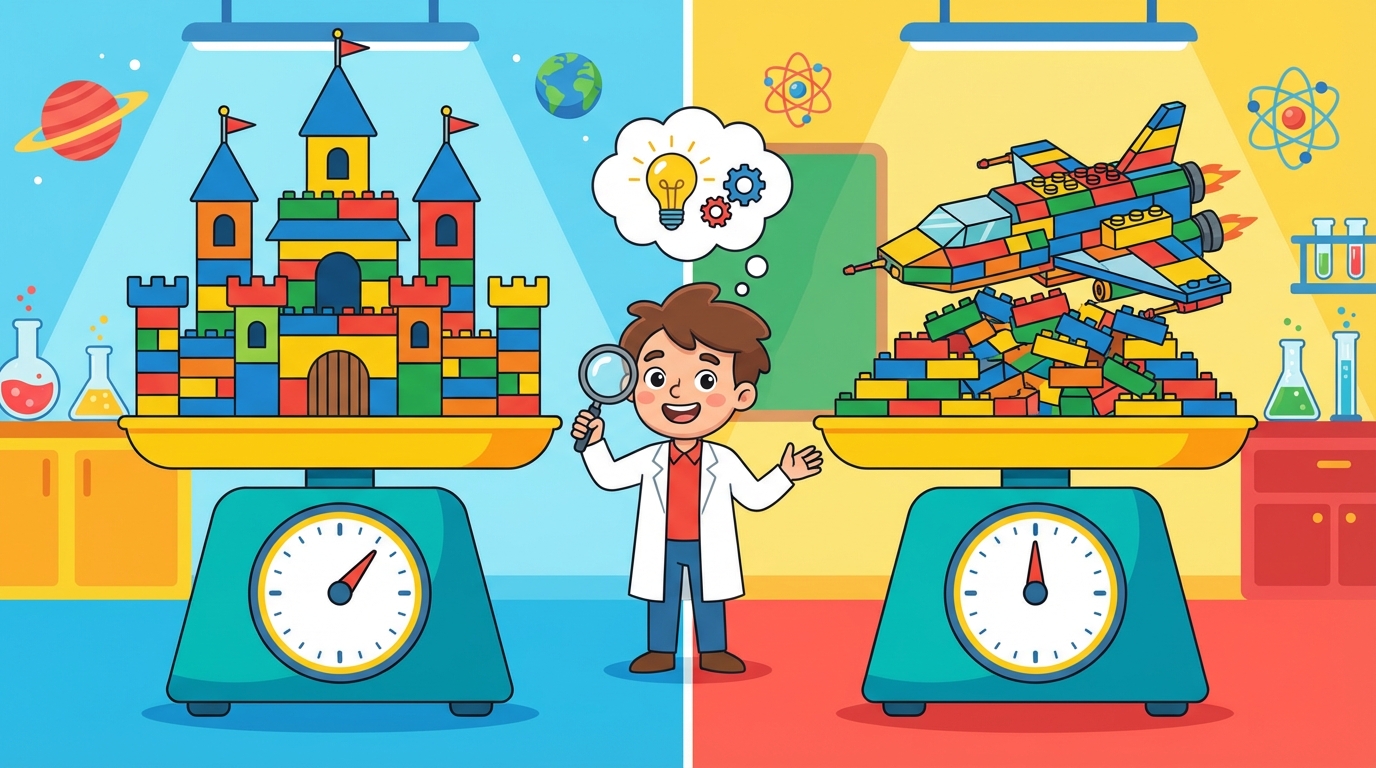

Is it Magic? No, it's Science!
Imagine you build a giant castle out of Lego bricks. If you take it apart and build a spaceship using every single piece, the weight (mass) of the spaceship will be exactly the same as the castle. Why? Because you didn't add or remove any bricks!
Matter is not created or destroyed. It only changes form.
🧪 Chemical Changes
This law applies to chemical reactions too. The stuff you start with (Reactants) must weigh the same as the stuff you end up with (Products).
Example: If you mix baking soda and vinegar in a sealed bag, the bag stays the same weight, even though gas is created!
🔥 The Campfire Mystery
When wood burns, it turns into a small pile of ash. Did the mass disappear? No!
Most of the wood turned into smoke and gases (Carbon Dioxide and Water Vapor) that floated away. If you caught all that smoke in a giant balloon, the total mass would equal the original wood.
| Phase | What Happens? | Total Mass |
|---|---|---|
| Before (Reactants) | Ingredients separately (Flour + Sugar + Eggs) | 1000 grams |
| Action | Mixing and Baking 🎂 | --- |
| After (Products) | Finished Cake + Water vapor lost | 1000 grams |
Key Facts
10 Key Vocabulary
Master these important terms for your exam:
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
|
Matter
Materia |
Anything that has mass and takes up space.
Cualquier cosa que tiene masa y ocupa espacio. |
|
Mass
Masa |
The amount of matter in an object.
La cantidad de materia en un objeto. |
|
Volume
Volumen |
The amount of space an object occupies.
La cantidad de espacio que ocupa un objeto. |
|
Density
Densidad |
The amount of mass in a given volume; it determines if an object sinks or floats.
La cantidad de masa en un volumen dado; determina si un objeto se hunde o flota. |
|
Atom
Átomo |
The smallest unit of an element that maintains the properties of that element.
La unidad más pequeña de un elemento que mantiene las propiedades de ese elemento. |
|
Solid
Sólido |
A state of matter with a definite shape and a definite volume.
Un estado de la materia con una forma definida y un volumen definido. |
|
Liquid
Líquido |
A state of matter with a definite volume but no definite shape.
Un estado de la materia con un volumen definido pero sin forma definida. |
|
Gas
Gas |
A state of matter with no definite shape and no definite volume.
Un estado de la materia sin forma definida y sin volumen definido. |
|
Physical Property
Propiedad física |
A characteristic that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's identity.
Una característica que se puede observar o medir sin cambiar la identidad de la sustancia. |
|
Chemical Property
Propiedad química |
A characteristic that describes a substance's ability to change into a new substance.
Una característica que describe la capacidad de una sustancia para transformarse en una nueva sustancia. |
|
Solubility
Solubilidad |
The ability of a substance to dissolve in another substance.
La capacidad de una sustancia para disolverse en otra sustancia. |
|
Conductivity
Conductividad |
The ability of a material to allow heat or electricity to flow through it.
La capacidad de un material para permitir que el calor o la electricidad fluyan a través de él. |
|
Magnetism
Magnetismo |
A physical property that refers to the ability to attract certain metals.
Una propiedad física que se refiere a la capacidad de atraer ciertos metales. |
|
Melting Point
Punto de fusión |
The temperature at which a solid becomes a liquid.
La temperatura a la cual un sólido se convierte en líquido. |
|
Boiling Point
Punto de ebullición |
The temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas.
La temperatura a la cual un líquido se convierte en gas. |
|
Displacement
Desplazamiento |
A method used to measure the volume of an irregularly shaped object by submerging it in water.
Un método utilizado para medir el volumen de un objeto de forma irregular sumergiéndolo en agua. |
Time to Practice!
There are 7 questions waiting for you. Questions are shuffled each attempt.
Take the Quiz